
![]() Insights
Insights
International
When creating a new language site, many companies do not localise URL structures. Whilst some companies may be unaware of the importance of URL localisation, others may simply miss them during content exports.
In this blog post, we examine why URL structures matter for user experience and SEO on new language sites, and how to incorporate special characters that you may find in different languages. We also look at how optimising and localising for different search engines in different markets affects the best practice advice you should follow.
URL stands for ‘Uniform Resource Locator’ and indicates the location of a web resource. Moz defines a URL as consisting of ‘a protocol, domain name, and path (which includes the specific subfolder structure where a page is located) and having the following basic format: protocol://domain-name.top-level-domain/path.’
There are several benefits for SEO and user experience by structuring and localising URLs correctly.
When a URL contains keywords that are both relevant to a page’s content and in the right language for the searcher, it provides a trust signal that the site is genuine and trustworthy. It also gives both users and search engines an indication of a page’s content.
It is vital that English keywords are not translated word-for-word as these may not be the same words that other language users search for. A simple example of this is UK users would look for a page that sells jumpers compared to US users who would look for a page that sells sweaters. When you incorporate another language into this scenario you can see how quickly your website could appear untrustworthy by using the wrong terminology or keywords in the wrong language. By using the wrong terms, you also limit the ability of your website to be found in search engine results. You can read more about the importance of local market keyword research in this blog post.
All of the above ultimately impacts on the click-through rate and bounce rate of your site from organic search, which will have an impact on your positions in SERPs (search engine results pages).
In addition to this, an experiment by our sister company, Search Laboratory, showed that URL structure does have a minor impact on rankings. The impact on SEO is minor compared to many other technical aspects, so it isn’t worth creating long URLs just to incorporate multiple keywords. Instead, keep them user-friendly and reflect the page content using a similar structure to the page title.
All URLs should ideally follow a parent-child structure. For example, your parent page may be a top-level category page, such as www.company.com/womenswear, and your child page a related sub-category page, such as one for dresses www.company.com/womenswear/dresses. Structuring your website and URLs this way allows you to build up the relevancy of your category pages and improve ranking positions.
Keywords in a URL highlight to a user that your page is relevant for what they are searching for. It also highlights to search engines that the page is relevant for the search query. When creating URLs for international websites, ensure your keywords are from local market keyword research, rather than translations of your English keywords. Avoid using English keywords for your international site unless users in that country specifically search in English.
For usability, it is best to aim for around 40-55 characters for a URL. As standard, some URLs may pull through numbers or codes. It is best, where possible, to use words rather than numbers but keep them as short as possible whilst providing meaning for users and search engines.
For readability and ranking purposes, we always advise clients to separate words in URLs with hyphens. Using spaces will result in ‘%20’ appearing throughout your URLs. If you opt for underscores instead, search engines may recognise it as being one word rather than two separate words, although search engines have gotten much better at recognising this in recent years.
Using inconsistent cases can cause problems with duplicate content if search engines think they refer to two separate pages e.g. website.com/womenswear vs website.com/Womenswear.
By packing URLs full of repetitive keywords or keywords that do not read naturally you risk impacting on both user experience and rankings. Users not clicking on a spammy URL can impact traffic to your website and your positions in the SERPs.
URL encoding converts characters into a format that can be transmitted over the internet. ASCII characters can be sent with no issues – ASCII characters include upper and lowercase English letter and numbers. Other characters from different languages need to be converted using URL encoding. By encoding characters, they will appear as a ‘%’ and two digits.
This list from Google shows the ASCII characters that can be used without encoding. Characters from the reserved set need to be used with care as they signal to Google various bits of information, for example ‘?’ represents the beginning of a query string.

Encoded accented characters tend to be supported by Google, but this doesn’t guarantee they will always work across all browsers. Some companies opt to ignore the accent and write it without in their URLs for this reason. Whilst it may be deemed safer to not use accented letters in URLs, in many instances removing accents can change the meaning of a word. This can create confusion as to the content behind a URL. For example, ‘té’ in Spanish means ‘tea’, whilst ‘te’ means ‘to you’. If this was used in a URL for a category page for tea, suddenly the page content becomes ambiguous which can affect relevancy for Google and user experience.
The other thing to consider is that by encoding an accented letter, URLs will display the unappealing % characters. For example, é will become %E9. Using accented letters can also create problems for reporting in tools such as Google Analytics.
Whilst there are pros and cons to both options, we recommend our clients use accented letters as this ensures no confusion as to the content of a page. This benefits click-through rates and user experience.
Google is not always the most dominant search engine in every country and, even when it is, there are sometimes other search engines with high market share. Here we will focus on how to structure URLs when targeting Baidu and Yandex.
Baidu is the most popular search engine in China. The Chinese language can pose a problem with URLs as Chinese characters are not recommended for URL structures. Search engines and browsers support the characters, but they can often be displayed as encoded characters, much like accented letters.
There are two alternatives to using Chinese characters. You can either use English words or Pinyin. Pinyin is the standard Chinese spelling system for writing Mandarin Chinese using the Roman alphabet.
We recommend that our clients use Pinyin for most words in Chinese URLs and separate words with a ‘-’ in the same way you would for Google. We recommend keeping English for simple or common words that would be easily understood by a Chinese audience, for example ‘ 新 闻 ’ could be written as ‘news’.
For URL structures, it is recommended to:
Yandex is a popular search engine in Russia with nearly 53% of search engine market share.
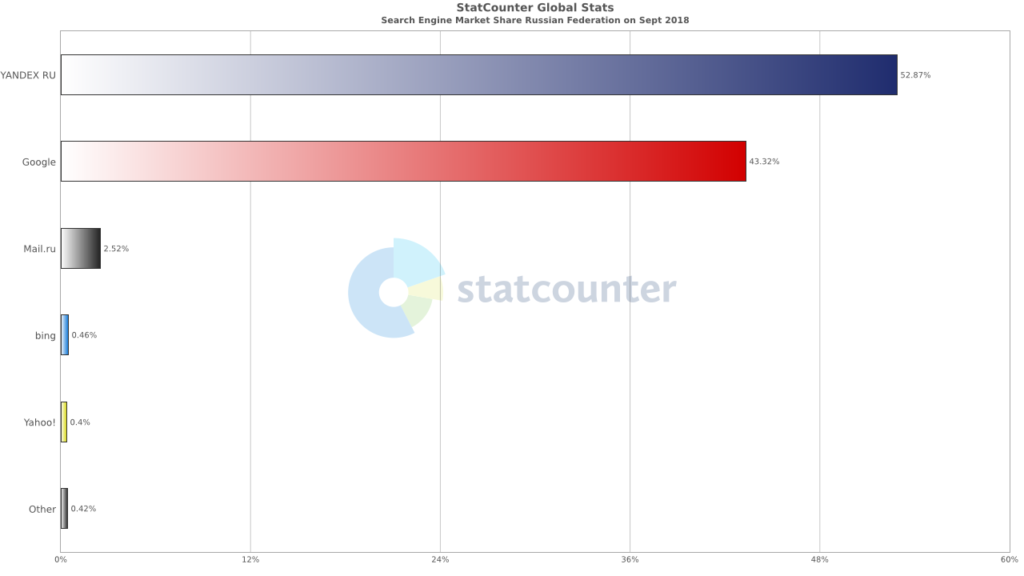
Source: http://gs.statcounter.com/search-engine-market-share/all/russian-federation/#monthly-201809-201809-bar
According to Yandex , ‘The URL should provide a clue about the page content.’ URLs can either be written in Cyrillic (a script the Russian language is based on) and encoded or transliterated into Latin characters as Yandex understands both. From our own work with clients, we have found that
similar search results were returned for both Latin and Cyrillic and many companies do use Latin transliteration in their URLs.
Keywords in URLs are seen as ‘ very important ’ for ranking in Yandex so it is a good idea to include these where possible.
If you need help localising URLs for international websites, speak to one of our team .
James Bentham and Amy Banks have co-authored The Future of SEO Report. The report analyses concerns and includes insights on how marketers can make sure their brand thrives in the evolving SEO landscape.
Topics covered in the report include the arrival of generative AI in search engines, the impact Google core updates have on results and how multichannel search is causing user journeys to become more fragmented.

![]() Insights
Insights

![]() Insights
Insights

![]() Insights
Insights